While power banks have advanced tremendously in terms of capacity and are now available in huge capacities, charging methods have also improved significantly, resulting in portable chargers depleting quickly. However, power bank batteries can drain rapidly for various reasons, which we’ll go over in this post. So without further ado, let’s get started.
Possible Causes for a Power Bank to Lose Charge Fast
1. You’re Using Fast-charging
 If both the power bank and the device being charged support rapid charging technologies such as Power Delivery or Qualcomm’s Quick Charge, the power bank’s battery will drain faster.
If both the power bank and the device being charged support rapid charging technologies such as Power Delivery or Qualcomm’s Quick Charge, the power bank’s battery will drain faster.
Quick charge speeds the charging process by boosting the charging voltage, resulting in an increase in wattage. In other words, electricity travels faster between the power bank and the other device, causing the power bank’s battery to drain more quickly.
2. You Have a Lightning Cable Always Connected
According to customer reports, when Lightning cables, especially USB-C to Lightning cables, are plugged into a power bank’s USB-C port, they drain a tiny amount of electricity, which can be enough to trick some power banks into remaining powered on and slowly discharge.
However, discharge caused by a connected USB-C to Lightning cable is only plausible with power banks equipped with low-current charging (trickle charging). The power banks that don’t have this feature automatically shut down the power supply under a specific value.
3. Damaged Battery
Any type of damage to the battery may result in the portable charger losing power faster than anticipated. If you recently dropped the power bank in water or on a hard surface or used it in extreme weather conditions (very cold or scorching), this might result in battery damage and capacity loss.
Consequently, you might notice that the battery drains more quickly than usual. Additionally, overcharging, over-discharging, and short-circuiting are all major problems resulting in severe battery damage. When these types of issues damage a battery, the power bank usually swells, which can lead to serious accidents including fires and explosions. This is why it’s crucial to examine the power bank for signs of damage.
4. The Battery is Close to its Maximum Lifespan
Lithium-ion batteries have a capacity of around 500 charges and discharges before losing about 20% of their capacity. Therefore, if you’re near this number, it’s common for the battery to drain more quickly than usual. It’s also worth mentioning that your charging routines have a significant influence on battery life.
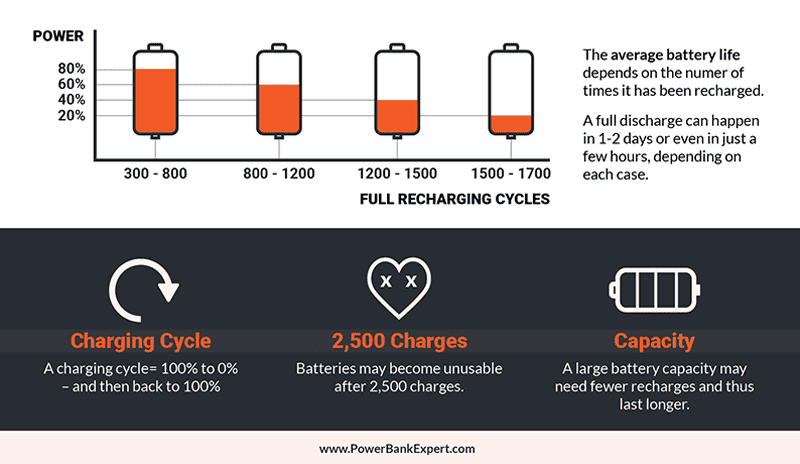
For example, if you totally discharge the battery and leave it that way for an extended period of time, the power bank will lose most of its capacity within a month or two. However, if you never discharge the power bank below 20% and never charge it beyond 85%, you will retain its battery’s full capacity even after 500 charges and discharges.
5. Difference Between the Advertised and Actual Capacity
Another thing you need to be aware of is the fact that the actual capacity of a power bank is lower than what’s advertised on the device. Tests have shown that a power bank’s advertised and actual capacity can differ by up to 40%, which is a significant difference.
As a result of this, customers might feel that the power bank battery is depleting too quickly. The reason for the difference between the advertised and actual capacity of the power bank is due to several factors, including the following:
- Lithium batteries in power banks operate at an average voltage of 3.7V, and the capacity advertised is based on this voltage. On the other hand, power banks must provide 5V output in order to charge USB-powered devices, thus converting 3.7V to 5V lowers the capacity of the power bank.
- Another issue is power loss. A converter circuit is used to convert the voltage between the power bank and the charged device. There is an initial power loss during the conversion from 3.7V to 5V. Additionally, extra power is lost during electricity transmission through the cable, decreasing the amount of charge you may anticipate receiving from the power bank.
If you’re interested in learning more about this subject, check out our dedicated article on this topic: Why is there a difference between real and rated battery capacity?
6. Faulty or Low-quality Charging Cable
Another common reason for power banks to drain their capacity fast is the internal resistance of the USB cable. Generally speaking, all cables have a resistance that causes power loss. But in most cases, this goes unnoticed because the lost values are very small. When it comes to faulty and counterfeit cables, their low quality results in increased power losses. The battery drains more because of the wasted electricity caused by power loss.
Best Practices to Prevent Fast Depletion of Power Bank Batteries
If you’re experiencing faster-than-usual depletion of your power bank’s battery, there are specific measures you can take to address this issue. These practices are aimed at reducing the rate at which your power bank loses charge, ensuring it retains power for when you need it most.
1. Optimize Charging Conditions
- Avoid Fast Charging When Not Necessary: If your power bank and device support fast charging, use this feature judiciously. Fast charging can lead to quicker depletion, so reserve it for when you need a quick power boost.
- Monitor Charging Environment: Charge your power bank in a cool, dry environment. High temperatures can increase the rate of battery depletion.
2. Cable Management
- Disconnect Cables When Not in Use: Unplug cables from the power bank when not charging a device. Even without a device attached, a connected cable can draw a small amount of power.
- Use High-Quality Cables: Ensure that the cables you use are of good quality and have low internal resistance to reduce power loss during charging.
3. Device Management
- Charge Efficiently: Avoid charging devices that are power-intensive or charging multiple devices simultaneously if your power bank is not designed for high output. This can drain the power bank faster.
- Monitor Connected Devices: Some devices may draw power even when fully charged or in standby mode. Disconnect devices once they are charged.
4. Power Bank Maintenance
- Regular Usage: Regularly use and recharge your power bank. Batteries can lose their efficiency if left discharged for extended periods.
- Check for Damage: Inspect your power bank for any signs of damage, such as swelling or leaks, which can affect its performance
