Although it’s not a common occurrence, power banks can swell up once the internal battery malfunctions. When this happens, they need to be treated with extra care as they’re in an unstable state. Swollen power banks should also be looked at as potential threats as if they deteriorate further, they can cause fires.
Why do Power Bank Batteries Get Bloated?
Power banks are basically Li-ion batteries with some circuitry, cased in a plastic or metal shell. So they’re predisposed to all shortcomings of Li-ion batteries in general. One of these is the fact that under some circumstances, Li-on batteries expand in volume, thus appearing bulkier.
This swelling happens due to an excess of current in the battery, which causes extra heat, which in turn causes gases from within the battery to expand their volume and thus expand the battery itself. As a result, the power bank becomes unstable, sometimes completely unusable, and in extreme cases, it might catch on fire or even explode.
There are multiple reasons for the current buildup that leads to the gas expansion within the power bank’s battery. For example, overcharging, overcurrent, or poor build quality can be determining factors that lead to a bloated power bank. This is why it’s always a good idea to purchase power banks from reputable brands that offer safety measures such as overcharge protection.
In some rare cases, the swelling doesn’t have an apparent reason. Batteries can pillow up by themselves even if left idle for long periods of time, without being subjected to overcharging, over-discharging, extreme temperatures, etc. This is why it’s always a good idea to simply check your power banks from time to time, especially if they’re not used on a current basis.
Chemical and Physical Processes
Early Signs of Battery Swelling
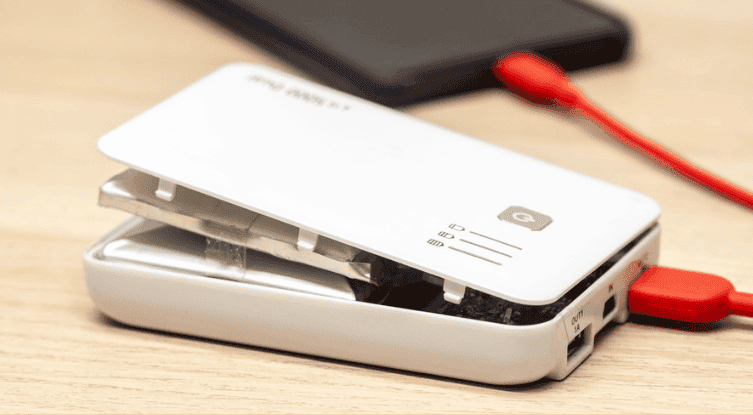

Sometimes the bloating effect is immediately visible, but other times it’s quite subtle and you need to look carefully in order to observe it. Here are some of the most common signs that the battery within the portable charger has started to swell:
- The power bank rocks on an even and smooth surface
- Uneven seams are visible on the outer side of the power bank
- You can see the edges of the power bank case lifting
- Notice any discoloration or deformation on the power bank’s surface
Early detection of swelling in power banks is critical for safety and maintaining the device’s longevity. Regular visual and tactile inspections, performance monitoring, and environmental awareness can help identify swelling at its onset. If any signs of swelling are detected, it is advised to stop using the power bank immediately and consult with a professional for advice on disposal or repair.
Can You Fix a Bulging Power Bank?
The swelling process in a battery is not reversible. So once it gets to this point there is no way to get it back to its original state. However, swollen power banks can theoretically be fixed, but the process requires replacing the bloated battery altogether. In some cases, this unfortunately might prove to be more expensive than purchasing a new device.
Please also note that fixing a swollen portable charger can be risky, even for professionals. Swollen batteries are unstable and dangerous to handle, and in many cases, it would be more prudent to replace the whole power bank rather than attempting to replace the battery.
Is a Swollen Power Bank Dangerous or Can You Still Use It?
As previously mentioned, yes, a swollen power bank can be dangerous since it can spontaneously combust or even explode. Even without an explosion, a swollen battery can leak corrosive and toxic chemicals. If these come into contact with your skin or eyes, they can cause injury.
Furthermore, using a portable charger with a swollen battery can potentially cause a short circuit or fire, especially when the device is charging or under high load. For these reasons, a swollen power bank should not be used and should be properly disposed of as soon as possible.
How To Safely Handle Bloated Power Bank
How To Prevent a Power Bank From Becoming Swollen
In order to prevent bloating and swelling, some general good-practice actions need to be considered:
- Purchase from reputable brands
- Make sure it comes with safety features (overcharge, overcurrent, short-circuit protection, etc)
- Don’t keep it plugged in once it’s fully charged
- Do not leave it under direct sunlight or intense heat
- Use a compatible adaptor for charging
- Replace it if it’s at the end of its lifecycle
- Do not pour liquids or submerge it
When it comes to charging power banks, they should not be charged at ambient temperatures lower than 32°F (0°C) or higher than 113-122°F (45-50°C). Charging at a high temperature decreases the life cycle and poses a safety hazard for the user.
However, charging at low temperatures can cause the growth in Lithium metal dendrites consequently causing an internal short circuit followed by the destruction of the battery and potentially triggering a fire.
Storage guidelines for power banks require it to be stored at or around room temperature (20-25°C / 68-77°F) at 20–40% state of charging. They have a very low self-discharge rate so they can be stored for long periods of time with minimal charge loss.
Most manufacturers also implement a minimal charging cut-off limit in order to keep power banks in a partially discharged state with enough current reserve so that they do not over-discharge.
Storing power banks at high temperatures or while it is fully charged should be avoided as it will place stress on the cell, decrease battery life, and increase the risk of explosion in case of an accident.
It should be noted that most users will never need to worry about this. Most environments in which users would be charging their power banks (homes, offices, etc.) will naturally fall within the safe temperature range.
Wrap-up
Swollen power banks should be a factor of concern for any user. Although they don’t present an immediate risk, they should be considered as potentially dangerous devices. The best course of action is to either take them to a dedicated electronics preparation shop or dispose of them in a responsible manner. Like in many other cases, implementing some simple good practices will prevent almost all power banks from ever reaching the bloated stage.
